|

Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2), now in Beta
testing, includes the new Windows Firewall, previously known as the
Internet Connection Firewall (ICF). Windows Firewall is a stateful
host-based firewall that drops all unsolicited incoming traffic
that does not correspond to either traffic sent in response to a
request of the computer (solicited traffic) or unsolicited traffic
that has been specified as allowed (excepted traffic). Windows
Firewall provides a level of protection from malicious users and
programs that rely on unsolicited incoming traffic to attack
computers on a network.
In Windows XP SP2, there are many new features for
Windows Firewall, including the following:
- Enabled by default for all the connections of the computer
- New global configuration options that apply to all
connections
- New set of dialog boxes for local configuration
- Excepted traffic can be specified by scope
- Excepted traffic can be specified by application filename
- Built-in support for Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
traffic
- New configuration options with Netsh and Group Policy
- New operating mode
- Enabled by default for all the connections of the computer
-
Startup security
This manual describes in detail the set of dialog
boxes to manually configure the new Windows Firewall. Unlike ICF in
Windows XP (prior to SP2), the configuration dialog boxes configure
both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic.
The settings for ICF in Windows XP (prior to SP2)
consist of a single checkbox (the Protect my computer and network
by limiting or preventing access to this computer from the Internet
check box on the Advanced tab of the properties of a connection)
and a Settings button from which you can configure excepted
traffic, logging settings, and allowed ICMP traffic.
In Windows XP SP2, the check box on the Advanced tab of the
properties of a connection has been replaced with a Settings button
from which you can configure general settings, permissions for
programs and services, connection-specific settings, log settings,
and allowed ICMP traffic. The Settings button launches the new
Windows Firewall Control Panel applet, which is also available from
the Network and Internet Connections and Security Center categories
of Control Panel.
The new Windows Firewall dialog box contains the following
tabs:
- General
- Exceptions
- Advanced
General Tab
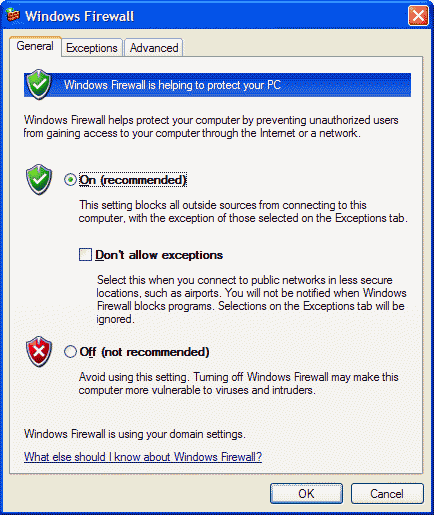
The General tab with its default settings is
shown in picture 1.
|
| Picture 1
|
- On (recommended)
Select to enable Windows Firewall for all of the network
connections that are selected on the Advanced tab. Windows Firewall
is enabled to allow only solicited and excepted incoming traffic.
Excepted traffic is configured on the Exceptions tab.
- Don’t allow exceptions
Click to allow only solicited incoming traffic. Excepted incoming
traffic is not allowed. The settings on the Exceptions tab are
ignored and all of the network connections are protected,
regardless of the settings on the Advanced tab.
- Off (not recommended)
Select to disable Windows Firewall. This is not recommended,
especially for network connections that are directly accessible
from the Internet, unless you are already using a third-party host
firewall product.
Notice that the default setting for Windows
Firewall is On (recommended) for all the connections of a computer
running Windows XP SP2 and for newly created connections. This can
impact the communications of programs or services that rely on
unsolicited incoming traffic. In this case, you must identify those
programs that are no longer working and add them or their traffic
as excepted traffic. Many programs, such as Internet browsers and
email clients (such as Outlook Express), do not rely on unsolicited
incoming traffic and operate properly with Windows Firewall
enabled.
If you are using Group Policy to configure Windows Firewall for
computers running Windows XP SP2, the Group Policy settings you
configure might not allow local configuration. In this case, the
options on the General tab and the other tabs might be grayed out
and unavailable, even when you log on with an account that is a
member of the local Administrators group (a local
administrator).
Group Policy-based Windows Firewall settings allow you to configure
a domain profile (a set of Windows Firewall settings that are
applied when you are attached to a network that contains domain
controllers) and standard profile (a set of Windows Firewall
settings that are applied when you are attached to a network that
does not contain domain controllers, such as the Internet). The
configuration dialog boxes only display the Windows Firewall
settings of the currently applied profile. To view the settings of
the profile that are not currently applied, use netsh firewall show
commands. To change the settings of the profile that are not
currently applied, use netsh firewall set commands.
Exceptions Tab
The Exceptions tab with its default settings
is shown in picture 2.

|
| Picture 2
|
From the Exceptions tab, you can enable or disable an existing
program or service or maintain the list of programs and services
that define excepted traffic. The excepted traffic is not allowed
when the Don’t allow exceptions option is selected on the General
tab.
With Windows XP (prior to SP2), you could define the excepted
traffic only in terms of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) ports. With Windows XP SP2, you can
define excepted traffic in terms of TCP and UDP ports or by the
file name of a program or service. This configuration flexibility
makes it easier to configure excepted traffic when the TCP or UDP
ports of the program or service are not known or are dynamically
determined when the program or service is started.
There are a set of preconfigured programs and services, which
include:
- File and Print Sharing
- Remote Assistance (enabled by default)
- Remote Desktop
- UPnP framework
These predefined programs and services cannot be deleted.
If allowed by Group Policy, you can create additional exceptions
based on specifying a program name by clicking Add Program and
exceptions based on specifying a TCP or UDP port by clicking
AddPort.
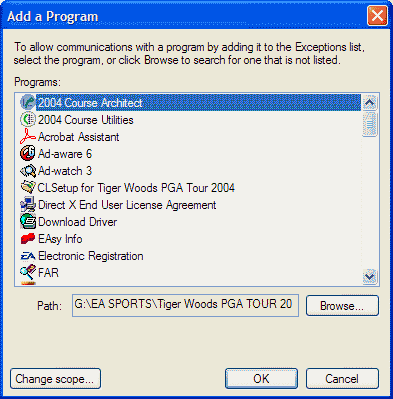
When you click Add Program, the Add Program dialog box is displayed
from which you can select a program or browse for a program’s file
name. An example is shown in picture 3.
|
| Picture 3
|
When you click AddPort, the Add a Port dialog box
is displayed, from which you can configure a TCP or UDP port. An
example is shown in picture 4.

|
| Picture 4
|
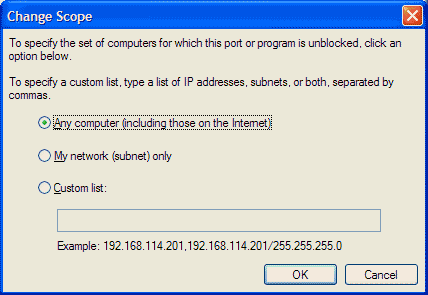
The new Windows Firewall allows you to specify the scope of
excepted traffic. The scope defines the portion of the network from
which the excepted traffic is allowed to originate. To define the
scope for a program or port, click Change Scope. An example
is shown in picture 5.
|
| Picture 5
|
You have three options when defining the scope for a program or
a port:
- Any computer (including those on the Internet)
Excepted traffic is allowed from any IPv4 address. This setting
might make your computer vulnerable to attacks from malicious users
or programs on the Internet.
- My network (subnet) only
Excepted traffic is allowed only from an IPv4 address that matches
the local network segment (subnet) to which the network connection
that received the traffic is attached. For example, if the network
connection is configured with an IPv4 address of 192.168.0.99 with
a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0, excepted traffic is only allowed from
IPv4 addresses in the range 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254.
- Custom list
You can specify one or more IPv4 addresses or IPv4 address ranges
separated by commas. IPv4 address ranges typically correspond to
subnets. For IPv4 addresses, type the IPv4 address in dotted
decimal notation. For IPv4 address ranges, you can specify the
range using a dotted decimal subnet mask or a prefix length. When
you use a dotted decimal subnet mask, you can specify the range as
an IPv4 network ID (such as 10.47.81.0/255.255.255.0) or by using
an IPv4 address within the range (such as
10.47.81.231/255.255.255.0). When you use a network prefix length,
you can specify the range as an IPv4 network ID (such as
10.47.81.0/24) or by using an IPv4 address within the range (such
as 10.47.81.231/24). An example custom list is the following:
10.91.12.56, 10.7.14.9/255.255.255.0, 10.116.45.0/255.255.255.0,
172.16.31.11/24, 172.16.111.0/24.
The My network (subnet) only scope is useful when you
want to allow access to a program or service for the computers on a
local home network that are all connected to the same subnet, but
not to potentially malicious Internet users.
Once the program or port is added, it is disabled by default in the
Programs and Services list.
All of the programs or services enabled from the Exceptions tab are
enabled for all of the connections that are selected on the
Advanced tab.
Advanced Tab
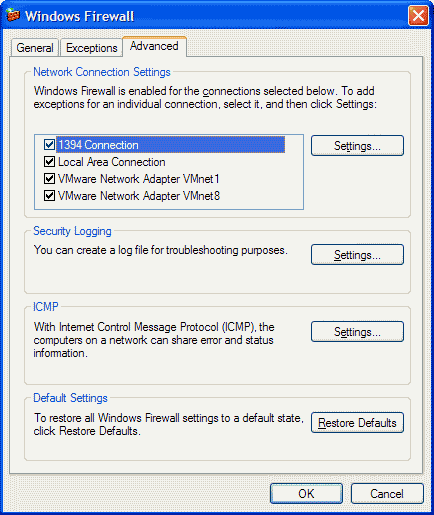
The Advanced tab is shown in picture 6.
|
| Picture 6
|
The Advanced tab contains the following sections:
- Network Connection Settings
- Security Logging
- ICMP
- Default Settings
Network Connections Settings
In Network Connection Settings, you can:
- Specify the set of interfaces on which Windows Firewall is
enabled. To enable, select the check box next to the network
connection name. To disable, clear the check box. By default, all
of the network connections have Windows Firewall enabled. If a
network connection does not appear in this list, then it is not a
standard networking connection. Examples include some custom
dialers from Internet service providers (ISPs).
- Configure advanced settings of an individual network connection
by clicking the network connection name, and then clicking
Settings.
If you clear all of the check boxes in the Network Connection
Settings, then Windows Firewall is not protecting your
computer, regardless of whether you have selected On
(recommended) on the General tab. The settings in
Network Connection Settings are ignored if you have selected
Don’t allow exceptions on the General tab, in which
case all interfaces are protected.
When you click Settings, the Advanced Settings dialog
box is displayed, as shown in picture 7.

|
| Picture 7
|
From the Advanced Settings dialog box, you can configure
specific services from the Services tab (by TCP or UDP port
only) or enable specific types of ICMP traffic from the ICMP
tab. These two tabs are equivalent to the settings tabs for ICF
configuration in Windows XP (prior to SP2).
Security Logging
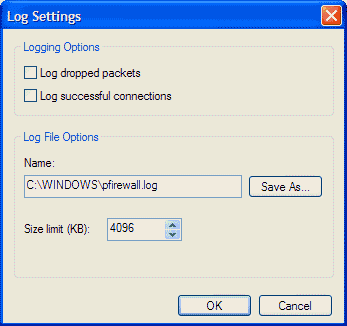
In Security Logging, click Settings to specify the
configuration of Windows Firewall logging in the Log
Settings dialog box, as shown in picture 8.
|
| Picture 8
|
From the Log Settings dialog box, you can configure
whether to log discarded (dropped) packets or successful
connections and specify the name and location of the log file (by
default set to Systemroot\pfirewall.log) and its maximum
size.
ICMP
In ICMP, click Settings to specify the types of ICMP
traffic that are allowed in the ICMP dialog box, as shown in
picture 9.

|
| Picture 9
|
From the ICMP dialog box, you can enable and disable the
types of incoming ICMP messages that Windows Firewall allows for
all the connections selected on the Advanced tab. ICMP
messages are used for diagnostics, reporting error conditions, and
configuration. By default, no ICMP messages in the list are
allowed.
A common step in troubleshooting connectivity problems is to use
the Ping tool to ping the address of the computer to which you are
trying to connect. When you ping, you send an ICMP Echo message and
get an ICMP Echo Reply message in response. By default, Windows
Firewall does not allow incoming ICMP Echo messages and therefore
the computer cannot send an ICMP Echo Reply in response. To
configure Windows Firewall to allow the incoming ICMP Echo message,
you must enable the Allow incoming echo request setting.
Default Settings
Click Restore Defaults to reset Windows Firewall back to its
originally installed state. When you click Restore Defaults,
you are prompted to verify your decision before Windows Firewall
settings are changed.
For more information
For more information about Windows XP SP2, consult the following
resources:
|










